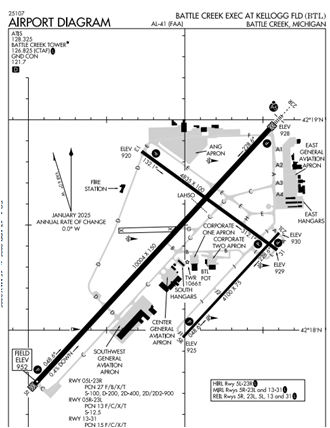
 A parallel runway at a heavily used training airport significantly enhances safety by segregating traffic, reducing congestion, and minimizing collision risks. Training airports host numerous student pilots practicing takeoffs, landings, and touch-and-go maneuvers, which increase runway occupancy time and airspace complexity. A parallel runway allows simultaneous operations, separating training flights from other traffic, such as commercial or general aviation, thereby reducing the likelihood of conflicts.
A parallel runway at a heavily used training airport significantly enhances safety by segregating traffic, reducing congestion, and minimizing collision risks. Training airports host numerous student pilots practicing takeoffs, landings, and touch-and-go maneuvers, which increase runway occupancy time and airspace complexity. A parallel runway allows simultaneous operations, separating training flights from other traffic, such as commercial or general aviation, thereby reducing the likelihood of conflicts.
Parallel runways enable air traffic controllers to assign dedicated runways for training activities. Student pilots, who may have slower response times or less predictable maneuvers, can operate on one runway, while more experienced pilots or larger aircraft use the other. This segregation minimizes the risk of runway incursions, where an aircraft inadvertently enters an active runway, a critical concern at busy training airports.
Parallel runways alleviate congestion. Training flights often involve repetitive circuits, leading to high traffic density. A single runway can become a bottleneck, increasing the chance of go-arounds or mid-air collisions in the pattern. Dual runways distribute this load, allowing smoother flow and reducing controller workload, which enhances situational awareness and decision-making.
Parallel runways provide operational flexibility during adverse conditions. For instance, if one runway is closed due to maintenance or weather, training can continue on the other, maintaining safety without halting operations. This redundancy is vital for airports with high training volumes.
Parallel runways also support emergency preparedness. In case of an incident, such as a gear-up landing, the unaffected runway ensures continued safe operations. By reducing traffic conflicts, easing congestion, and offering operational resilience, parallel runways create a safer environment for training airports, protecting both novice pilots and the broader aviation community.
At airports, especially those that have busy training operations, a parallel runway can allow air traffic control to separate faster inbound and outbound traffic, such as jets, from those that are slower and needing to do multiple takeoff and landing operations. The ability to separate dissimilar aircraft operations onto different runways allows ATC to provide better traffic separation and increase safety.
There is no doubt that an airport with a well-run parallel runway operation increases safety and allows for greater efficiency in flight training operations. Training at an airport like this is a significant benefit when it is available.